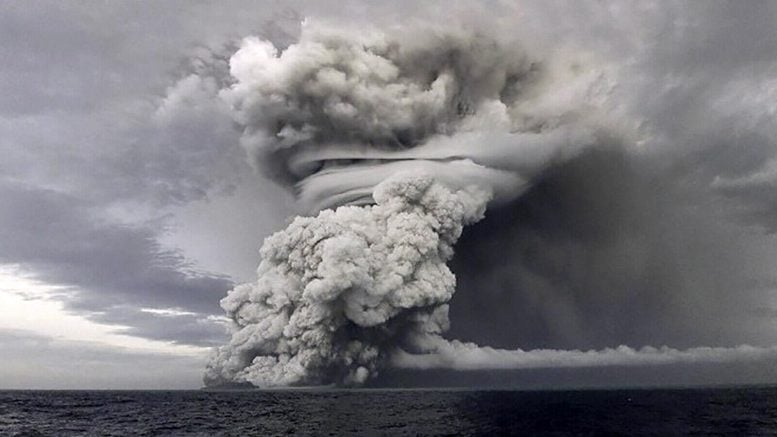

Widely thought to be responsible for Earth’s extreme warmth during the past two years, researchers say the Hunga Tonga eruption actually cooled the climate.
Research by Texas A&M University explores the 2022 Hunga Tonga volcano eruption’s climate effects, discovering that it caused cooling rather than warming. This contradicts earlier beliefs and stresses the need for continued satellite data to understand climate dynamics, reinforcing the dominant role of human-induced emissions in climate change.
A collaborative research team, including Texas A&M University atmospheric scientist Dr. Andrew Dessler, is investigating the climatic effects of the 2022 Hunga Tonga volcano eruption, simultaneously challenging previously held assumptions about its impact.
The remarkable two-day event, which occurred in mid-January 2022, injected vast amounts of volcanic aerosols and water vapor into the atmosphere. Historically, large volcanic eruptions like Tambora in 1815 and Mt. Pinatubo in 1991 have led to significant cooling effects on the global climate by blocking sunlight with their aerosols. However, Hunga Tonga’s eruption presented a unique scenario: As a submarine volcano, it introduced an unprecedented amount of water vapor into the stratosphere, increasing total stratospheric water content by about 10%.
Because water vapor is a powerful greenhouse gas, Dessler says there was initial speculation that it might account for the extreme global warmth in 2023 and 2024. Instead, the results of the team’s research, published on July 24 in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, reveal the opposite: The eruption actually contributed to cooling the Earth, similar to other major volcanic events.
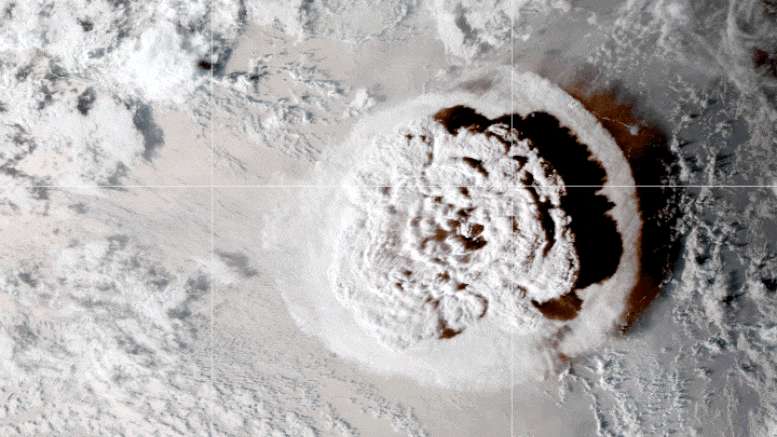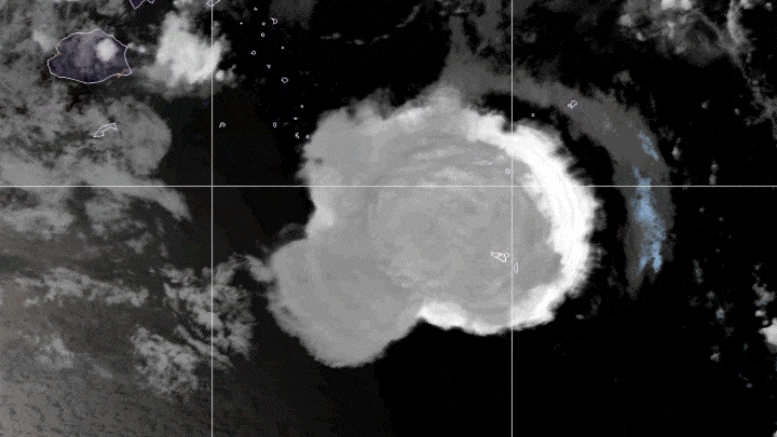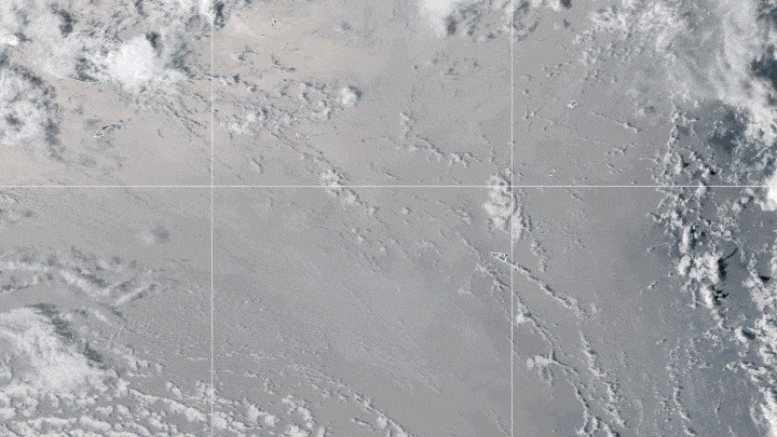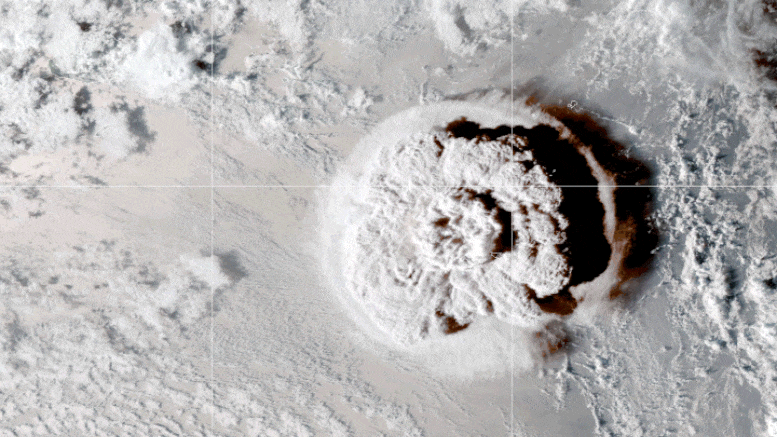
A Volcanic Eruption’s Cooling Effect
The team’s paper, titled “Evolution of the Climate Forcing During the Two Years after the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Eruption,” includes insight and analysis from Dessler, a professor in the Texas A&M Department of Atmospheric Sciences and the director of the Texas Center for Climate Studies; first author Dr. Mark Schoeberl, chief scientist at the Virginia-based Science and Technology Corporation in Hamburg, Virginia; and multiple scientists from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
Their methodology involved analyzing NASA and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) satellite data observations of aerosols and water vapor, among other variables, to estimate the energy balance of the Earth’s climate system. Their analysis revealed that the eruption resulted in more energy leaving the climate system than entering it, thereby inducing the slight cooling effect.
“Our paper pours cold water on the explanation that the eruption caused the extreme warmth of 2023 and 2024,” Dessler explained. “Instead, we need to focus primarily on greenhouse gases from human activities as the main cause of the warming, with a big assist from the ongoing El Nino.”
Implications And Future Research
According to Dessler, this research has important implications for both scientists and the general public. By dismissing the volcanic eruption as a major factor in the recent warming, the team’s study reinforces his point that human-induced greenhouse gas emissions are the primary driver of climate change. This focus is particularly relevant, given the ongoing debate and misinformation about the causes of global warming.
Moreover, Schoeberl says the study underscores the importance of continued investment in satellite-based stratospheric measurements.
“Our understanding of the Hunga Tonga eruption is largely thanks to the investment in stratospheric satellite measurements by NOAA and NASA over the past two decades,” Schoeberl added. “However, we need to be cautious about a potential ‘stratospheric data desert,’ as some of the most critical instruments are not being replaced.”
Unresolved Questions and the Path Forward
While this paper answers several important questions, Dessler acknowledges that it simultaneously introduces new ones. For instance, the researchers highlighted some unresolved issues related to the Hunga Tonga eruption, such as the unexpectedly low levels of sulfur dioxide produced by such a violent eruption and the minimal impact the eruption had on the 2023 ozone hole. The 2023 ozone hole refers to a significant thinning of the ozone layer over Antarctica, which allows more harmful UV radiation to reach the Earth’s surface. Additionally, the persistence of water vapor in the stratosphere beyond what was predicted by models suggests that there is still much to learn about stratospheric circulation processes.
As scientists work to resolve ongoing questions and deepen our understanding of the stratosphere, Schoeberl says the team’s work highlights the critical need for continued research and precise data to tackle the challenges of climate change.
Reference: “Evolution of the Climate Forcing During the Two Years After the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Eruption” by M. R. Schoeberl, Y. Wang, G. Taha, D. J. Zawada, R. Ueyama and A. Dessler, 24 July 2024, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres.
DOI: 10.1029/2024JD041296
6 Comments
More proof they have 0 clue what they are talking about. Humans cannot simply will the climate to get cooler no matter what we do. While I think we should be environmentally responsible, this climate change is responsible for everything is a big sham.
Amen. Go look at Andrew Dessler’s X profile. His timeline is full of Biden posts and he seems to hate anyone right of woke. I would never call Dessler a doctor.
The corollary to ‘Identity Politics’ is ‘Identity Science.’
There have been quite a few peer reviewed studies on the Tonga Volcano. All have suggested that it is difficult to determine which had greater effect: The cooling due to Sulfur Dioxide, or the warming due to the unusually large amount of water vapor. By my tally, there is no consensus, but there have been slightly more studies arriving at a SLIGHT warming effect in the Southern Hemisphere and a slight cooling effect in the Northern Hemisphere.
what’s of concern to me is how warm would it have been without the eruption.
“Instead, we need to focus primarily on greenhouse gases from human activities as the main cause of the warming…” This is coming from people who have no idea how the earth and its environment really work. Of course, we need more research money for more high-tech detectors. “Schoeberl says the study underscores the importance of continued investment in satellite-based stratospheric measurements.” Yeah, right.