
Researchers have unveiled the dynamical nature of emergent magnetic monopoles in real magnets for the first time.
Magnetic monopoles are elementary particles with isolated magnetic charges in three dimensions. In other words, they behave as isolated north or south poles of a magnet. Magnetic monopoles have attracted continuous research interest since physicist Paul Dirac’s first proposal in 1931.
However, real magnetic monopoles have not yet been observed and their existence remains an open question. On the other hand, scientists have discovered quasi-particles that mathematically behave as magnetic monopoles in condensed matter systems, resulting in interesting phenomena.
Recently, researchers discovered that a material called manganese germanide (MnGe) has a unique periodic structure, formed by special magnetic configurations called hedgehogs and antihedgehogs, which is called a magnetic hedgehog lattice. In these special configurations, the magnetic moments point radially outward (hedgehog) or inward (antihedgehog), resembling the spines of a hedgehog. These hedgehogs and antihedgehogs act like magnetic monopoles and antimonopoles, serving as sources or sinks of emergent magnetic fields.
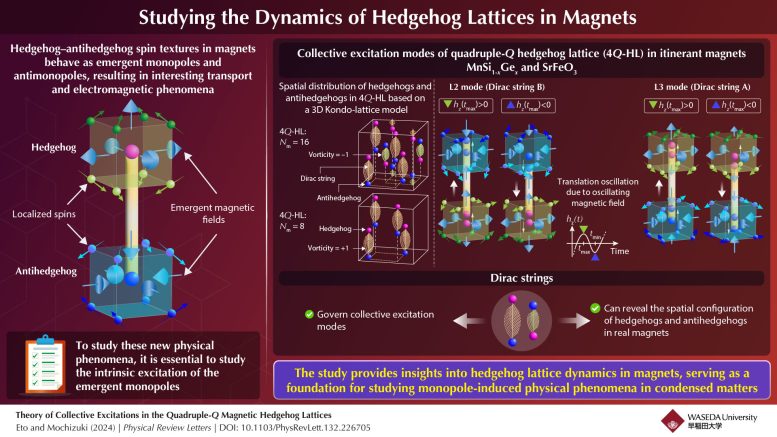
MnGe exhibits what is known as a triple-Q hedgehog lattice. However, recent experiments have shown that the substitution of Ge with Si (MnSi1-xGex) transforms the arrangement into the quadruple-Q hedgehog lattice (4Q-HL). This new arrangement, also found in the perovskite ferrite SrFeO3, provides a promising avenue for studying and controlling the properties of hedgehog lattices. Moreover, these magnetic monopoles can also induce electric fields through moving following Maxwell’s laws of electromagnetism. To understand the resulting new physical phenomena, it is essential to study the inherent excitations of hedgehog lattices.
Research Findings from Waseda University
In a recent study, Professor Masahito Mochizuki and Ph.D. course student Rintaro Eto, both from the Department of Applied Physics at Waseda University, theoretically studied the collective excitation modes of 4Q-HLs in MnSi1-xGex and SrFeO3. “Our research clarified the unknown dynamical nature of emergent magnetic monopoles in magnetic materials for the first time. This can inspire future experiments on hedgehog-hosting materials with applications in electronic devices and for bridging particle physics and condensed-matter physics,” says Mochizuki. Their study was published in the journal Physical Review Letters on 31 May 2024.
Utilizing the three-dimensional Kondo-lattice model, the researchers reproduced the two distinct 4Q-HLs found in MnSi1-xGex and SrFeO3 and analyzed their dynamical properties. They discovered that the 4Q-HLs have collective excitation modes associated with the oscillation of Dirac strings. A Dirac string is a theoretical concept in quantum mechanics that describes a string that connects a magnetic monopole and a magnetic antimonopole, in this case, a hedgehog and an antihedgehog.
The researchers found that the number of these excitation modes depends on the number and configuration of Dirac strings, offering a way to experimentally determine the spatial configuration of hedgehogs and antihedgehogs and their unique topology in real magnets such as MnSi1-xGex and SrFeO3. This finding offers insights into the dynamics of hedgehog lattices in other magnets as well. Moreover, the finding enables us to switch on and off the excitation modes through controlling the presence or absence of the Dirac strings with external magnetic field.
Explaining the significance of their results, Eto remarks, “The collective spin excitation modes revealed in the study are elementary excitations that directly reflect the presence (or absence) of emergent magnetic monopoles. Thus, our findings will be a fundamental guideline for studying the more detailed dynamical nature of emergent monopoles in magnetic materials in the future. Moreover, they might become the building blocks of novel field-switchable spintronic devices such as nano-sized power generators, light-voltage converters, and light/microwave filters based on emergent electromagnetism.”
These discoveries have the potential to open new research avenues in fundamental physics and lead to the development of new technologies involving emergent magnetic monopoles in magnets.
Reference: “Theory of Collective Excitations in the Quadruple-𝑄 Magnetic Hedgehog Lattices” by Rintaro Eto and Masahito Mochizuki, 31 May 2024, Physical Review Letters.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.226705
2 Comments
Researchers have identified new dynamic properties in these structures, potentially paving the way for innovative technologies in spintronics and fundamental physics research.
Please ask the researcher to think,
1. Why do electrons spin?
2. If a magnetic monopole is a physical reality, what are the dimensions of its spacetime structure?
3. Are the physical phenomena observed in scientific experiments natural properties of matter?
Learning widely from others’ strong points may inspire you. If researchers are willing to further consider, you can browse https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/701333717 and https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/463666584.
Good luck to the researchers.
Intelligent chips, batteries, and communication based on topological vortex self-organization are the key areas that contemporary science should focus on.