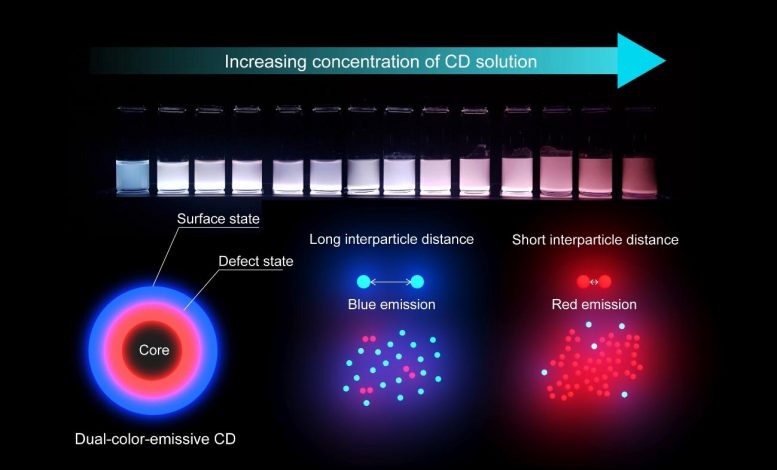
KAIST researchers have synthesized a collection of nanoparticles, known as carbon dots, capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of light from a single particle. Additionally, the team discovered that the dispersion of the carbon dots, or the interparticle distance between each dot, influences the properties of the light the carbon dots emit. The discovery will allow researchers to understand how to control these carbon dots and create new, environmentally responsible displays, lighting, and sensing technology.
Research into nanoparticles capable of emitting light, such as quantum dots, has been an active area of interest for the last decade and a half. These particles, or phosphors, are nanoparticles made out of various materials that are capable of emitting light at specific wavelengths by leveraging quantum mechanical properties of the materials. This provides new ways to develop lighting and display solutions as well as more precise detection and sensing in instruments.
As technology becomes smaller and more sophisticated, the usage of fluorescent nanoparticles has seen a dramatic increase in many applications due to the purity of the colors emitting from the dots as well as their tunability to meet desired optical properties.
Carbon dots, a type of fluorescent nanoparticles, have seen an increase in interest from researchers as a candidate to replace non-carbon dots, the construction of which requires heavy metals that are toxic to the environment. Since they are made up of mostly carbon, the low toxicity is an extremely attractive quality when coupled with the tunability of their inherent optical properties.
Another striking feature of carbon dots is their capability to emit multiple wavelengths of light from a single nanoparticle. This multi-wavelength emission can be stimulated under a single excitation source, enabling the simple and robust generation of white light from a single particle by emitting multiple wavelengths simultaneously.
Carbon dots also exhibit a concentration-dependent photoluminescence. In other words, the distance between individual carbon dots affects the light that the carbon dots subsequently emit under an excitation source. These combined properties make carbon dots a unique source that will result in extremely accurate detection and sensing.
This concentration-dependency, however, had not been fully understood. In order to fully utilize the capabilities of carbon dots, the mechanisms that govern the seemingly variable optical properties must first be uncovered. It was previously theorized that the concentration-dependency of carbon dots was due to a hydrogen bonding effect.
Now, a KAIST research team, led by Professor Do Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has posited and demonstrated that the dual-color-emissiveness is instead due to the interparticle distances between each carbon dot. The research was published in the 36th Issue of Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics.
First author of the paper, PhD candidate Hyo Jeong Yoo, along with Professor Kim and researcher Byeong Eun Kwak, examined how the relative light intensity of the red and blue colors changed when varying the interparticle distances, or concentration, of the carbon dots. They found that as the concentration was adjusted, the light emitted from the carbon dots would transform. By varying the concentration, the team was able to control the relative intensity of the colors, as well as emit them simultaneously to generate a white light from a single source (See Figure).
“The concentration-dependence of the photoluminescence of carbon dots on the change of the emissive origins for different interparticle distances has been overlooked in previous research. With the analysis of the dual-color-emission phenomenon of carbon dots, we believe that this result may provide a new perspective to investigate their photoluminescence mechanism,” Yoo explained.
The newly analyzed ability to control the photoluminescence of carbon dots will likely be heavily utilized in the continued development of solid-state lighting applications and sensing.
Reference: “Interparticle distance as a key factor for controlling the dual-emission properties of carbon dots” by Hyo Jeong Yoo, Byeong Eun Kwak and Do Hyun Kim, 25 June 2020, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics.
DOI: 10.1039/D0CP02120B
2 Comments
I notice the trolls commenting on the perceived futility and wastefulness of dark matter research and theory are conspicuously absent from this article because this kind of research will likely result in next-level visual graphics in existing applications such as tv and devices, as well as fantasies such as wearable, programmable graphic tee shirts, and MAGA hats, and fairly quickly. Imagine a wallpaper one could change graphics on with one’s device, or even stream or cast content upon.
Actually already imagined by the likes of Phillip K. Dick {Total Recall, or, for purists, Reality Inc} and the “Back to the Future II” movie, years ago.