Are there anti-stars around us? Answer from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope.
What if some of the antimatter that was thought to have disappeared was lurking around us in the form of anti-stars? Scientists from the Institute for Research in Astrophysics and Planetology (IRAP – CNRS/CNES/UT3 Paul Sabatier) are using the Fermi gamma-ray space telescope to put the most constraining limits ever on this hypothesis.
What is antimatter? Although it is often associated with the world of science fiction, antimatter does indeed exist. It is observed in outer space and in physics laboratories. It is a state symmetrical to the ordinary matter we know. According to the laws of physics known to date, the Universe should contain equal amounts of matter and antimatter. However, today antimatter is only found at the trace level, and research suggests that the entire Cosmos is devoid of it. This is presently regarded as one of the greatest mysteries of the Universe.
Nonetheless, the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) particle detector on board the International Space Station (ISS) recently appears to indicate that there could be more antimatter around us than we thought. This might be hiding in the vicinity of our solar system in the form of unlikely objects: stars made of antimatter, or anti-stars.[1] The existence of such objects would have serious consequences on our understanding of the Universe, but how do we test this bold hypothesis?

It is known that the collision between antimatter and matter produces gamma rays, the most energetic form of radiation. This is why, in a paper published in the journal Physical Review D, IRAP researchers used ten years of data from the Fermi gamma-ray space telescope to estimate the maximum number of anti-stars in our Galaxy.[2]
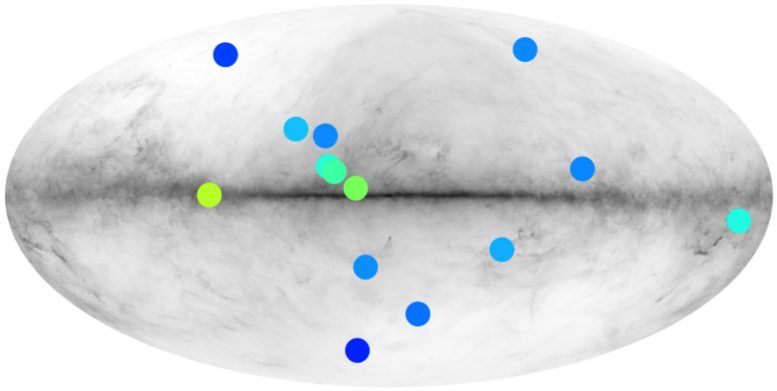
They were able to isolate fourteen candidates whose emission properties are comparable to those expected for antistars in the catalog of gamma-ray sources found by Fermi. However, the nature of these sources is still unconfirmed. It is much more likely that they are actually pulsars, black holes, or other types of well-established gamma-ray emitters.
The IRAP team then estimated the maximum number of anti-stars that could exist in our Galaxy, resulting in the strongest constraints ever. By imagining that they are distributed like ordinary stars, mostly in the galactic disk, they were able to establish that there is at most one antistar for every 300,000 ordinary stars.
Nevertheless, they also showed that old anti-stars, whose origin would go back to the beginnings of the Universe, could more easily hide from gamma-ray telescopes in the halo around the Galaxy.
References:
- “Where do the AMS-02 antihelium events come from?” by Vivian Poulin, Pierre Salati, Ilias Cholis, Marc Kamionkowski and Joseph Silk, 28 January 2019, Physical Review D.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevD.99.023016 - “Constraints on the antistar fraction in the Solar System neighborhood from the 10-year Fermi Large Area Telescope gamma-ray source catalog” by Simon Dupourqué, Luigi Tibaldo and Peter von Ballmoos, 20 April 2021, Physical Review D.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevD.103.083016