
Scientists reveal that the deterioration of modern concrete and asphalt structures is due to the presence of trace quantities of organic matter in these structures.
Cement and asphalt are vital to modern construction materials; cement is used for the construction of various buildings and structures, while asphalt is primarily used for highways and runways. They have been widely used for these purposes since the 1800s. It has been observed modern concrete structures and asphalt structures tend to deteriorate much faster than historical structures, but the reason for this phenomenon was unknown.
A team of scientists from six institutions, including Akihiro Moriyoshi, Emeritus Professor Hokkaido University, have revealed that the presence of trace quantities of organic matter in modern concrete structures and asphalt pavements drive the deterioration of these structures. Their findings, which include novel methods to assess deterioration, were published in the journal PLOS ONE.
The deterioration of modern concrete structures and asphalt pavements are a major issue. The features that lead to deterioration include cracks, disaggregation (breakdown into fine white powder) and delamination (separation into layers). These deteriorated structures are unsafe for their intended purposes; rapid deterioration reduces the expected lifespan of structures, thereby increasing the costs for maintenance or replacement.
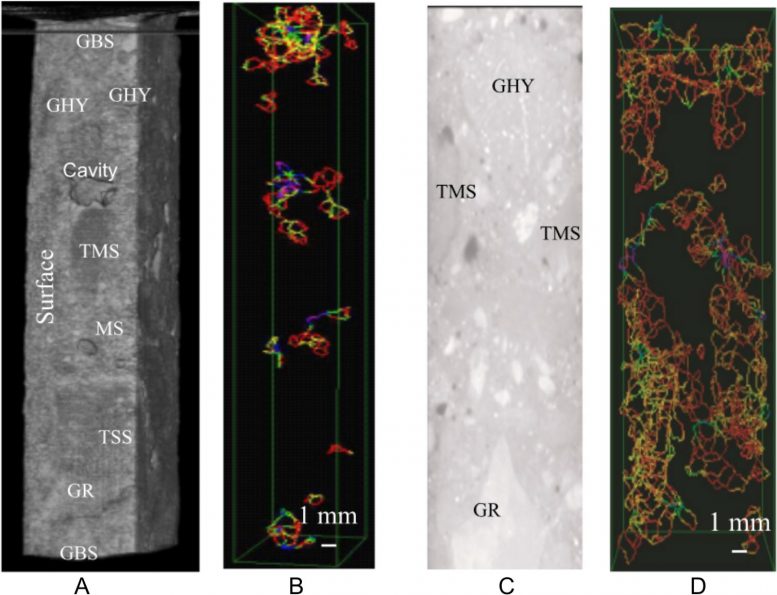
The scientists set out to develop a new method to assess the rate of deterioration in concrete. The current method is based on the width of surface cracks in concrete and a simple chemical test; however, it only gives an incomplete picture of the level of damage. During their experiments, the scientists happened to notice that a strange odor developed when commercial cement was mixed with water. They hypothesized that organic matter was responsible for the odor, and investigated the effect it has on the deterioration of concrete.

The scientists developed the one-dimensional transient moisture permeation apparatus to accurately reproduce the field environmental conditions that concrete structures and asphalt pavements are exposed to, in the laboratory, over a period of 24 hours. When combined with CT scans, this method can be used to evaluate the precise extent of the damage. They tested a variety of asphalt samples from Japan dating back to 1960; a number of concrete samples from across the world were also tested, and a 120-year-old concrete sample was used as a reference.
The scientists showed that there are a number of organic molecules, from diverse sources, present in modern concrete structures and asphalt pavements: phthalates, diesel exhaust particulates, surfactants, and windshield washer fluids. These molecules are either introduced during the manufacturing process — the contents of phthalates, phosphate compounds, and AE water reducing agents present in commercially available cements are 0.0012%, 0.12%, and 0.25%, respectively — or absorbed from the environment, and cause rapid deterioration of concrete structures and asphalt pavements.
Of the organic matter present in cement, phthalates have the highest effect on deterioration more than phosphates and AE water reducing agents. Organic matter in water accelerates the deterioration of asphalt pavements. The scientists also showed that crack width and length is the best determinant of concrete damage, while the degree of formation of amorphization is the best determinant of deterioration. They believe that their findings can be used to develop novel formulations for long-lasting concrete structures and asphalt pavements.
Reference: “Deterioration of modern concrete structures and asphalt pavements by respiratory action and trace quantities of organic matter” by Akihiro Moriyoshi, Eiji Shibata, Masahito Natsuhara, Kiyoshi Sakai, Takashi Kondo and Akihiko Kasahara, 13 May 2021, PLOS ONE.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249761