
Analysis of a sample from asteroid Bennu found essential life components and hints of a watery past, offering insights into solar system origins and prebiotic chemistry.
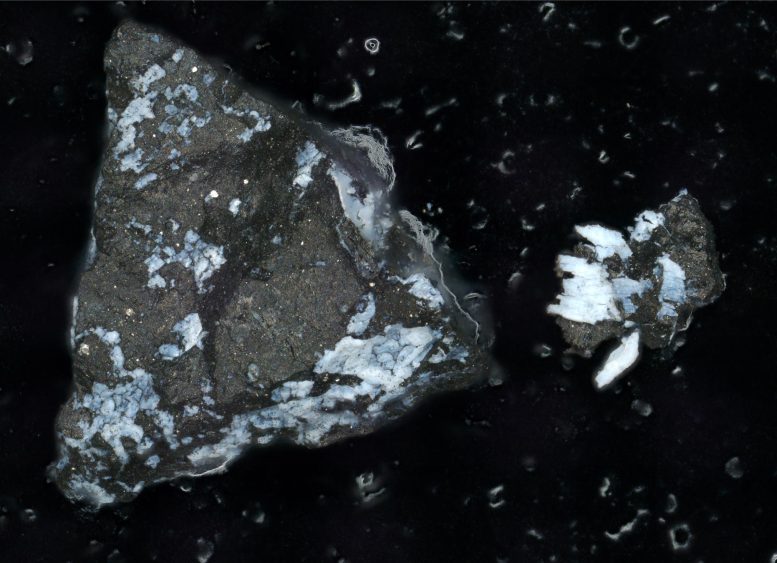
- Early analysis of the asteroid Bennu sample returned by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission has revealed dust rich in carbon, nitrogen, and organic compounds, all of which are essential components for life as we know it. Dominated by clay minerals, particularly serpentine, the sample mirrors the type of rock found at mid-ocean ridges on Earth.
- The magnesium-sodium phosphate found in the sample hints that the asteroid could have splintered off from an ancient, small, primitive ocean world. The phosphate was a surprise to the team because the mineral had not been detected by the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft while at Bennu.
- While a similar phosphate was found in the asteroid Ryugu sample delivered by JAXA’s (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Hayabusa2 mission in 2020, the magnesium-sodium phosphate detected in the Bennu sample stands out for its purity (that is, the lack of other materials included in the mineral) and the size of its grains, unprecedented in any meteorite sample.
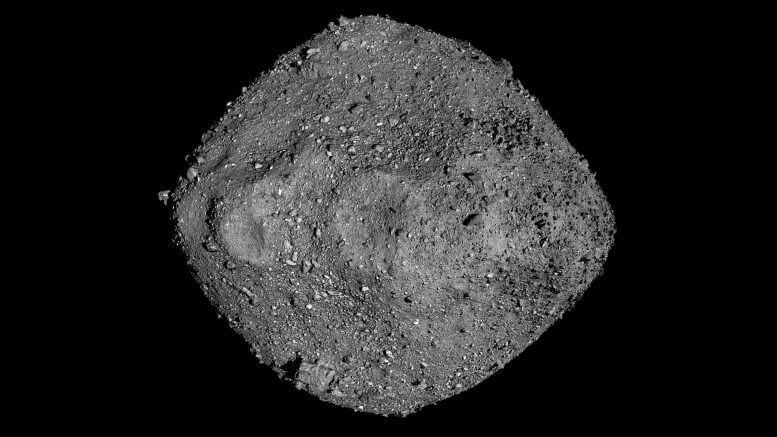

Discoveries From Asteroid Bennu’s Composition
Scientists have eagerly awaited the opportunity to dig into the 4.3-ounce (121.6-gram) pristine asteroid Bennu sample collected by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security – Regolith Explorer) mission since it was delivered to Earth last fall. They hoped the material would hold secrets of the solar system’s past and the prebiotic chemistry that might have led to the origin of life on Earth. An early analysis of the Bennu sample, published recently in Meteoritics & Planetary Science, demonstrates this excitement was warranted.
The OSIRIS-REx Sample Analysis Team found that Bennu contains the original ingredients that formed our solar system. The asteroid’s dust is rich in carbon and nitrogen, as well as organic compounds, all of which are essential components for life as we know it. The sample also contains magnesium-sodium phosphate, which was a surprise to the research team, because it wasn’t seen in the remote sensing data collected by the spacecraft at Bennu. Its presence in the sample hints that the asteroid could have splintered off from a long-gone, tiny, primitive ocean world.

Evidence of Water in Asteroid Materials
Analysis of the Bennu sample unveiled intriguing insights into the asteroid’s composition. Dominated by clay minerals, particularly serpentine, the sample mirrors the type of rock found at mid-ocean ridges on Earth, where material from the mantle, the layer beneath Earth’s crust, encounters water.
This interaction doesn’t just result in clay formation; it also gives rise to a variety of minerals like carbonates, iron oxides, and iron sulfides. But the most unexpected discovery is the presence of water-soluble phosphates. These compounds are components of biochemistry for all known life on Earth today.
While a similar phosphate was found in the asteroid Ryugu sample delivered by JAXA’s (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Hayabusa2 mission in 2020, the magnesium-sodium phosphate detected in the Bennu sample stands out for its purity — that is, the lack of other materials in the mineral — and the size of its grains, unprecedented in any meteorite sample.
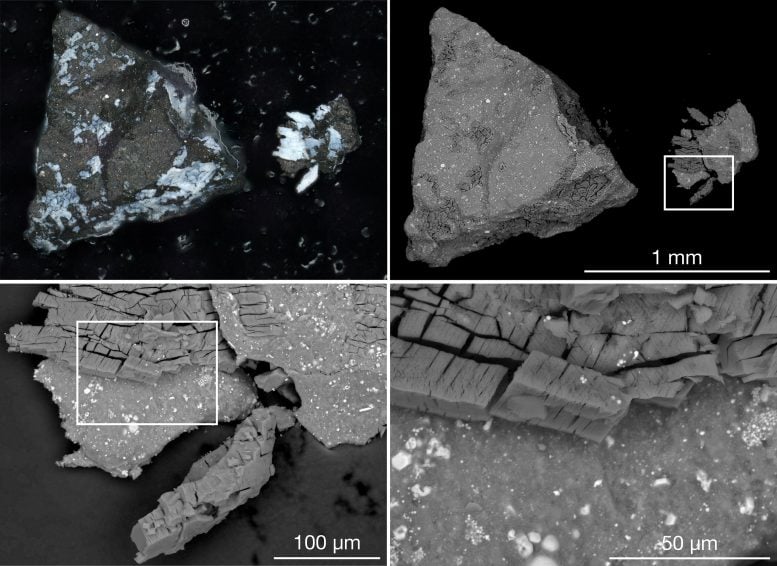

The finding of magnesium-sodium phosphates in the Bennu sample raises questions about the geochemical processes that concentrated these elements and provides valuable clues about Bennu’s historic conditions.
“The presence and state of phosphates, along with other elements and compounds on Bennu, suggest a watery past for the asteroid,” said Dante Lauretta, co-lead author of the paper and principal investigator for OSIRIS-REx at the University of Arizona, Tucson. “Bennu potentially could have once been part of a wetter world. Although, this hypothesis requires further investigation.”
“OSIRIS-REx gave us exactly what we hoped: a large pristine asteroid sample rich in nitrogen and carbon from a formerly wet world,” said Jason Dworkin, a co-author on the paper and the OSIRIS-REx project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Insights Into Early Solar System Conditions
Despite its possible history of interaction with water, Bennu remains a chemically primitive asteroid, with elemental proportions closely resembling those of the Sun.
“The sample we returned is the largest reservoir of unaltered asteroid material on Earth right now,” said Lauretta.
This composition offers a glimpse into the early days of our solar system, over 4.5 billion years ago. These rocks have retained their original state, having neither melted nor resolidified since their inception, affirming their ancient origins.
Hints at Life’s Building Blocks
The team has confirmed the asteroid is rich in carbon and nitrogen. These elements are crucial in understanding the environments where Bennu’s materials originated and the chemical processes that transformed simple elements into complex molecules, potentially laying the groundwork for life on Earth.
“These findings underscore the importance of collecting and studying material from asteroids like Bennu — especially low-density material that would typically burn up upon entering Earth’s atmosphere,” said Lauretta. “This material holds the key to unraveling the intricate processes of solar system formation and the prebiotic chemistry that could have contributed to life emerging on Earth.”
What’s Next
Dozens more labs in the United States and around the world will receive portions of the Bennu sample from NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in the coming months, and many more scientific papers describing analyses of the Bennu sample are expected in the next few years from the OSIRIS-REx Sample Analysis Team.
“The Bennu samples are tantalizingly beautiful extraterrestrial rocks,” said Harold Connolly, co-lead author on the paper and OSIRIS-REx mission sample scientist at Rowan University in Glassboro, New Jersey. “Each week, analysis by the OSIRIS-REx Sample Analysis Team provides new and sometimes surprising findings that are helping place important constraints on the origin and evolution of Earth-like planets.”
Launched on September 8, 2016, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft traveled to near-Earth asteroid Bennu and collected a sample of rocks and dust from the surface. OSIRIS-REx, the first U.S. mission to collect a sample from an asteroid, delivered the sample to Earth on September 24, 2023.
Reference: “Asteroid (101955) Bennu in the laboratory: Properties of the sample collected by OSIRIS-REx” by Dante S. Lauretta, Harold C. Connolly, Joseph E. Aebersold, Conel M. O’D. Alexander, Ronald-L. Ballouz, Jessica J. Barnes, Helena C. Bates, Carina A. Bennett, Laurinne Blanche, Erika H. Blumenfeld, Simon J. Clemett, George D. Cody, Daniella N. DellaGiustina, Jason P. Dworkin, Scott A. Eckley, Dionysis I. Foustoukos, Ian A. Franchi, Daniel P. Glavin, Richard C. Greenwood, Pierre Haenecour, Victoria E. Hamilton, Dolores H. Hill, Takahiro Hiroi, Kana Ishimaru, Fred Jourdan, Hannah H. Kaplan, Lindsay P. Keller, Ashley J. King, Piers Koefoed, Melissa K. Kontogiannis, Loan Le, Robert J. Macke, Timothy J. McCoy, Ralph E. Milliken, Jens Najorka, Ann N. Nguyen, Maurizio Pajola, Anjani T. Polit, Kevin Righter, Heather L. Roper, Sara S. Russell, Andrew J. Ryan, Scott A. Sandford, Paul F. Schofield, Cody D. Schultz, Laura B. Seifert, Shogo Tachibana, Kathie L. Thomas-Keprta, Michelle S. Thompson, Valerie Tu, Filippo Tusberti, Kun Wang, Thomas J. Zega, C. W. V. Wolner and , 26 June 2024, Meteoritics & Planetary Science.
DOI: 10.1111/maps.14227
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, provided overall mission management, systems engineering, and the safety and mission assurance for OSIRIS-REx. Dante Lauretta of the University of Arizona, Tucson, is the principal investigator. The university leads the science team and the mission’s science observation planning and data processing. Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, built the spacecraft and provided flight operations. Goddard and KinetX Aerospace were responsible for navigating the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. Curation for OSIRIS-REx takes place at NASA Johnson. International partnerships on this mission include the OSIRIS-REx Laser Altimeter instrument from CSA (Canadian Space Agency) and asteroid sample science collaboration with JAXA’s Hayabusa2 mission. OSIRIS-REx is the third mission in NASA’s New Frontiers Program, managed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.