
A fascinating feature takes center stage in this new image from ESA’s Mars Express: a dark, uneven scar slicing through marbled ground at the foot of a giant volcano.
This scar, known as Aganippe Fossa, is a patchy, roughly 600-km-long feature known as a ‘graben’: a ditch-like groove with steep walls on either side.
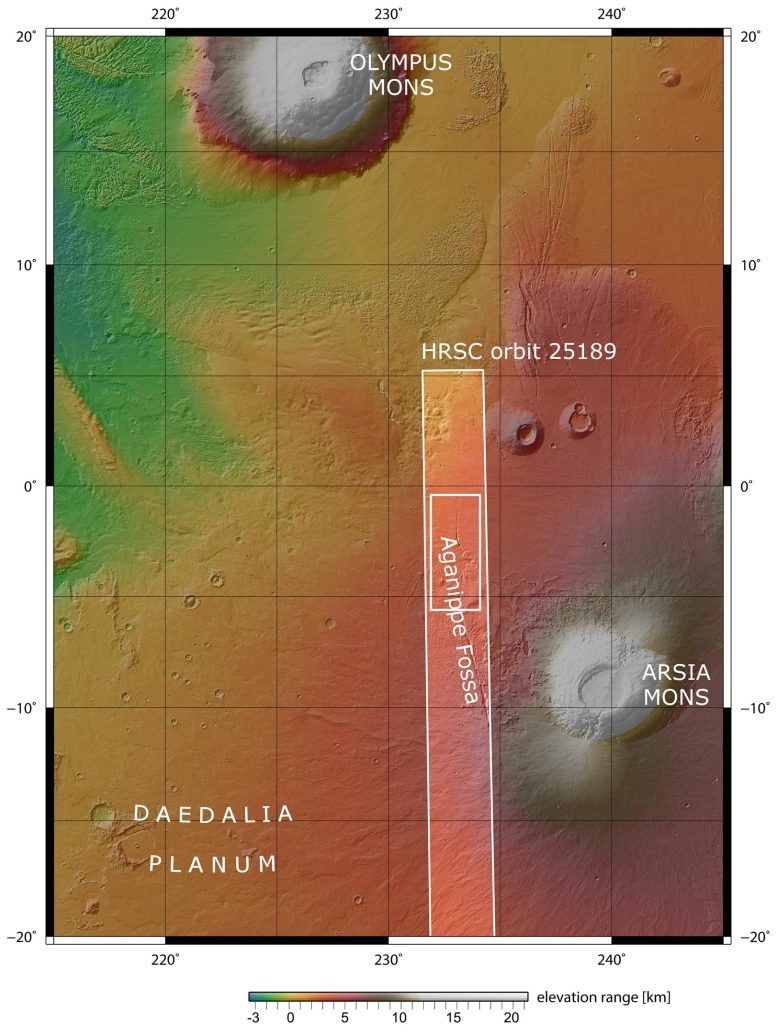
Aganippe Fossa cuts across the lower flank of one of Mars’s largest volcanoes, Arsia Mons. Mars Express regularly observes Arsia Mons and its nearby companions in the region of Tharsis, where several of Mars’s behemoth volcanoes are found. This includes Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano in the Solar System (visible in the context map associated with this new image, as is Arsia Mons).
Arsia Mons itself measures 435 km in diameter and rises more than 9 km above the surrounding plains. For context, the highest dormant volcano on Earth, Ojos del Salado on the Argentina-Chile border, tops out at under 7 km.
Seeping Lava
We’re still unsure of how and when Aganippe Fossa came to be, but it seems likely that it was formed as magma rising underneath the colossal mass of the Tharsis volcanoes caused Mars’s crust to stretch and crack.
In this view, Mars Express’s High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) captures two different kinds of terrain: so-called hummocky terrain, which comprises many irregularly shaped mounds and valleys all clustered together, and lobate terrain, which is formed of gently sloping cliffs and rocky debris.
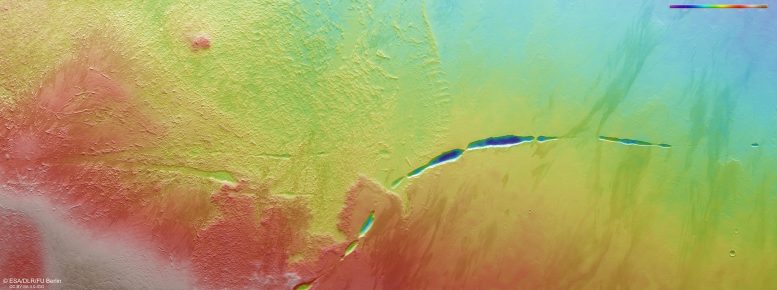
These terrains are characteristic of Arsia Mons’s ring-shaped ‘aureole’, a 100,000-square-kilometer disc around the base of the volcano, possibly associated with ancient glaciers. Intriguingly, this aureole has only built up on the northwestern flank of the volcano, likely due to prevailing winds from the opposite direction controlling where ice settled over time.
Windblown dust and sand have also shaped this patch of Mars, creating interesting zebra-like patterns to the right of the frame as darker material is deposited on lighter ground (or vice versa!). The surface here also shows evidence of lava flows, dating from when the volcano was active.

Exploring Mars
Mars Express has been orbiting the Red Planet since 2003. It is imaging Mars’s surface, mapping its minerals, identifying the composition and circulation of its tenuous atmosphere, probing beneath its crust, and exploring how various phenomena interact in the Martian environment.
The spacecraft’s HRSC, responsible for these images, has revealed much about Mars’s diverse surface in the past 20 years. Its images show everything from wind-sculpted ridges and grooves to sinkholes on the flanks of colossal volcanoes to impact craters, tectonic faults, river channels, and ancient lava pools. The mission has been immensely productive over its lifetime, creating a far fuller and more accurate understanding of our planetary neighbor than ever before.
The High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) on the Mars Express spacecraft is a sophisticated imaging system designed to study Mars in high detail. Launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2003, the HRSC captures high-resolution, three-dimensional images of the Martian surface, enabling scientists to examine the planet’s topography and morphology in unprecedented detail. This camera system uses stereo imaging techniques to produce color images along with topographic maps, helping researchers analyze the geology, composition, and physical processes of Mars. The HRSC has been instrumental in providing insights into the planet’s past water activity, volcanic activity, and other dynamic processes.