
Researchers at Newcastle University have created eco-friendly, high-efficiency photovoltaic cells for powering IoT devices using ambient light, achieving 38% power conversion efficiency. They also introduced an energy management technique using LSTM neural networks to optimize energy usage and minimize power losses.
Newcastle University researchers have created environmentally-friendly, high-efficiency photovoltaic cells that harness ambient light to power internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Led by Dr. Marina Freitag, the research group from the from School of Natural and Environmental Sciences (SNES) created dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells based on a copper(II/I) electrolyte, achieving an unprecedented power conversion efficiency of 38% and 1.0V open-circuit voltage at 1,000 lux (fluorescent lamp). The cells are non-toxic and environmentally friendly, setting a new standard for sustainable energy sources in ambient environments.
Published in the journal Chemical Science, the research has the potential to revolutionize the way IoT devices are powered, making them more sustainable and efficient, and opening up new opportunities in industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and smart city development.
Dr. Marina Freitag, Principal Investigator at SNES, Newcastle University, said: “Our research marks an important step towards making IoT devices more sustainable and energy-efficient. By combining innovative photovoltaic cells with intelligent energy management techniques, we are paving the way for a multitude of new device implementations that will have far-reaching applications in various industries.”
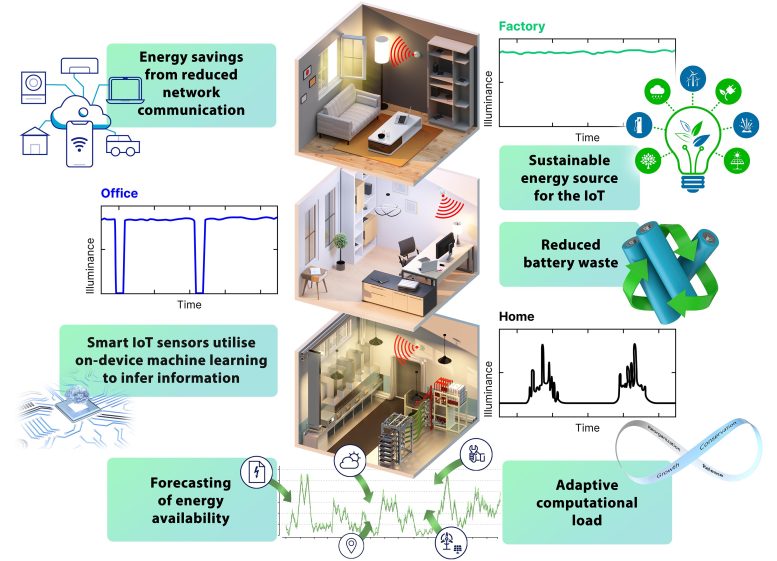
The team also introduced a pioneering energy management technique, employing long short-term memory (LSTM) artificial neural networks to predict changing deployment environments and adapt the computational load of IoT sensors accordingly. This dynamic energy management system enables the energy-harvesting circuit to operate at optimal efficiency, minimizing power losses or brownouts.
This breakthrough study demonstrates how the synergy of artificial intelligence and ambient light as a power source can enable the next generation of IoT devices. The energy-efficient IoT sensors, powered by high-efficiency ambient photovoltaic cells, can dynamically adapt their energy usage based on LSTM predictions, resulting in significant energy savings and reduced network communication requirements.
Reference: “Emerging Indoor Photovoltaics for Self-Powered and Self-Aware IoT towards Sustainable Energy Management” by Hannes Michaels, Michael Rinderle, Iacopo Benesperi, Richard Freitag, Alessio Gagliardi and Marina Freitag, 13 April 2023, Chemical Science.
DOI: 10.1039/d3sc00659j
1 Comment
“The cells are non-toxic and environmentally friendly, setting a new standard for sustainable energy sources in ambient environments.”
The fact that a copper-based electrolyte is used raises questions about just how benign the cells are. Metallic copper is used for its antibiotic properties, and copper sulfate is used to kill algae in reservoirs. But then, “The poison is in the dose.”