Japanese researchers have enhanced heat dissipation in nanodevices by adding a silicon dioxide coating to silicon structures, potentially revolutionizing the design and efficiency of future electronic devices.
Researchers from Japan have been working hard to keep their cool—or at least—keep their nanodevices from overheating. By adding a tiny coating of silicon dioxide to micro-sized silicon structures, they were able to show a significant increase in the rate of heat dissipated. This work may lead to smaller and cheaper electronic devices that can pack in more microcircuits.
As consumer electronics become ever more compact, while still boasting increased processing power, the need to manage waste heat from microcircuits has grown to become a major concern. Some scientific instruments and nanoscale machines require careful consideration of how localized heat will be shunted out of the device in order to prevent damage. Some cooling occurs when heat is radiated away as electromagnetic waves—similar to how the sun’s power reaches the Earth through the vacuum of space. However, the rate of energy transfer can be too slow to protect the performance of sensitive and densely packed integrated electronic circuits. For the next generation of devices to be developed, novel approaches may need to be established to address this issue of heat transmission.
Research Findings and Implications
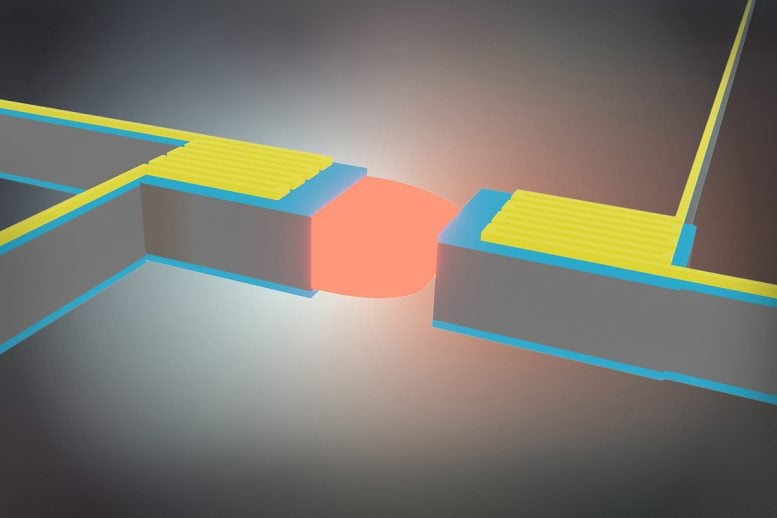
In a study recently published in the journal Physical Review Letters, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science at the University of Tokyo, showed how the rate of radiative heat transfer can be doubled between two micro-scale silicon plates separated by a tiny gap. The key was using a coating of silicon dioxide that created a coupling between the thermal vibrations of the plate at the surface (called phonons) and the photons (which make up the radiation).
“We were able to show both theoretically and experimentally how electromagnetic waves were excited at the interface of the oxide layer that enhanced the rate of heat transfer,” lead author of the study, Saeko Tachikawa says. The small size of the layers compared with the wavelengths of the electromagnetic energy and its attachment to the silicon plate, which carries the energy without loss, allowed the device to surpass the normal limits of heat transfer, and thus cool faster.
Because current microelectronics are already based on silicon, the findings of this research could be easily integrated into future generations of semiconductor devices. “Our work provides insight into possible heat dissipation management strategies in the semiconductor industry, along with various other related fields such as nanotech manufacturing,” says senior author, Masahiro Nomura. The research also helps to establish a better fundamental understanding of how heat transfer works at the nanoscale level, since this is still an area of active research.
Reference: “Enhanced Far-Field Thermal Radiation through a Polaritonic Waveguide” by Saeko Tachikawa, Jose Ordonez-Miranda, Laurent Jalabert, Yunhui Wu, Roman Anufriev, Yangyu Guo, Byunggi Kim, Hiroyuki Fujita, Sebastian Volz and Masahiro Nomura, 3 May 2024, Physical Review Letters.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.186904