
At the 2024 Consumer Electronics Show (CES), the spotlight was on groundbreaking developments in AI and healthcare. However, battery technology is the game-changer at the heart of these innovations, enabling greater power efficiency. Importantly, electric vehicles are where this technology is being applied most intensely.
Today’s EVs can travel around 700 km on a single charge, while researchers are aiming for a 1,000 km battery range. Researchers are fervently exploring the use of silicon, known for its high storage capacity, as the anode material in lithium-ion batteries for EVs. However, despite its potential, bringing silicon into practical use remains a puzzle that researchers are still working hard to piece together.
Breakthrough in Silicon-based Battery Technology
Enter Professor Soojin Park, PhD candidate Minjun Je, and Dr. Hye Bin Son from the Department of Chemistry at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH). They have cracked the code, developing a pocket-friendly and rock-solid next-generation high-energy-density Li-ion battery system using micro silicon particles and gel polymer electrolytes. This work was recently published in the journal Advanced Science.
Challenges With Silicon as a Battery Material
Employing silicon as a battery material presents challenges: It expands by more than three times during charging and then contracts back to its original size while discharging, significantly impacting battery efficiency. Utilizing nano-sized silicon (10-9m) partially addresses the issue, but the sophisticated production process is complex and astronomically expensive, making it a challenging budget proposition.
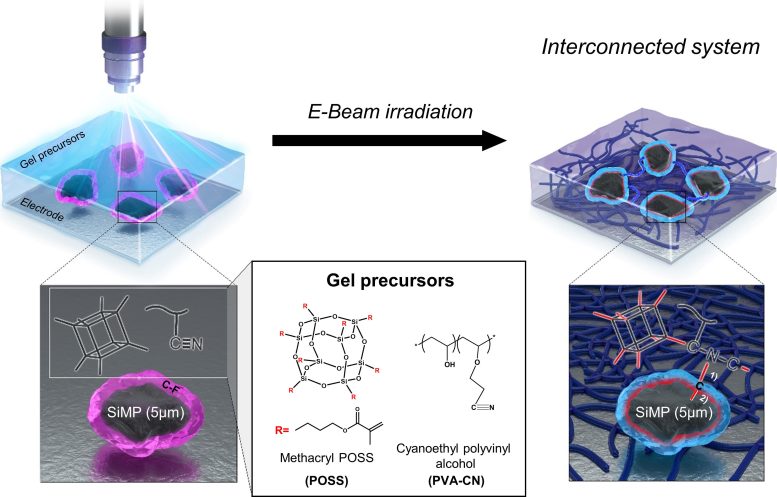
By contrast, micro-sized silicon (10-6m) is superbly practical in terms of cost and energy density. Yet, the expansion issue of the larger silicon particles becomes more pronounced during battery operation, posing limitations for its use as an anode material.
Innovations in Gel Polymer Electrolytes
The research team applied gel polymer electrolytes to develop an economical yet stable silicon-based battery system. The electrolyte within a lithium-ion battery is a crucial component, facilitating the movement of ions between the cathode and anode. Unlike conventional liquid electrolytes, gel electrolytes exist in a solid or gel state, characterized by an elastic polymer structure that has better stability than their liquid counterparts do.
Enhancing Battery Performance With Micro Silicon
The research team employed an electron beam to form covalent linkages between micro-silicon particles and gel electrolytes. These covalent linkages serve to disperse internal stress caused by volume expansion during lithium-ion battery operation, alleviating the changes in micro silicon volume and enhancing structural stability.
The outcome was remarkable: The battery exhibited stable performance even with micro silicon particles (5μm), which were a hundred times larger than those used in traditional nano-silicon anodes. Additionally, the silicon-gel electrolyte system developed by the research team exhibited ion conductivity similar to conventional batteries using liquid electrolytes, with an approximate 40% improvement in energy density. Moreover, the team’s system holds significant value due to its straightforward manufacturing process that is ready for immediate application.
Professor Soojin Park stressed: “We used a micro-silicon anode, yet, we have a stable battery. This research brings us closer to a real high-energy-density lithium-ion battery system.”
Reference: “Formulating Electron Beam-Induced Covalent Linkages for Stable and High-Energy-Density Silicon Microparticle Anode” by Minjun Je, Hye Bin Son, Yu-Jin Han, Hangeol Jang, Sungho Kim, Dongjoo kim, Jieun Kang, Jin-Hyeok Jeong, Chihyun Hwang, Gyujin Song, Hyun-Kon Song, Tae Sung Ha and Soojin Park, 17 January 2024, Advanced Science.
DOI: 10.1002/advs.202305298
This study was conducted with the support from the Independent Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
6 Comments
That secret ingredient is called “government subsidy”.
They keep talking about all this new battery technology, but I never see it for sale on Amazon, or anywhere else. Where is this technology? Why can’t I buy it? Is big oil getting in the way or something?
I believe Tesla covered using silicon during (battery day) they also bought out a company that was researching silicon batteries. There is also a company called Amprius with silicon batteries so far they are only selling them to the government. I know they all claim extreme gravimetric densities. Cost and longevity still has to be proven.
Most electric vehicles do 700km(about 430mls)that’s a joke.my daughters suv get about 175mls on a charge which I thought was pretty pathetic.
WTF is a Kilometer
Kilometer is metric system, you american guy should stop using imperial system already