The oldest fossil of a modern bird yet found, dating from the age of dinosaurs, has been identified by an international team of paleontologists.
The spectacular fossil, affectionately nicknamed the ‘Wonderchicken,’ includes a nearly complete skull, hidden inside nondescript pieces of rock, and dates from less than one million years before the asteroid impact which eliminated all large dinosaurs.
Writing in the journal Nature, the team, led by the University of Cambridge, believes the new fossil helps clarify why birds survived the mass extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous period, while the giant dinosaurs did not.
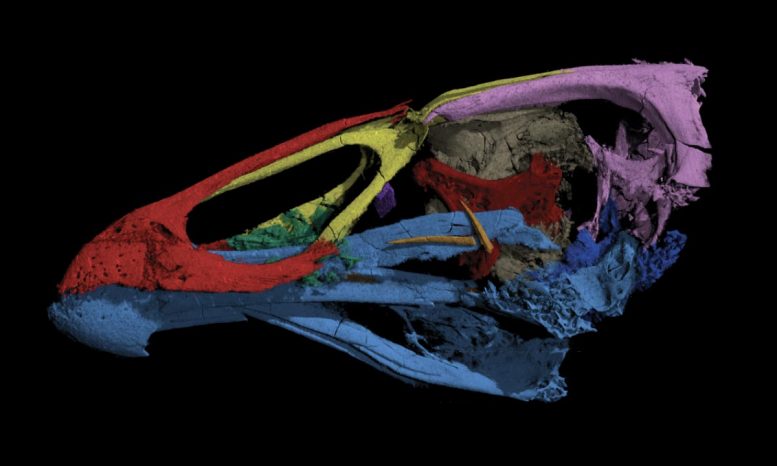
Detailed analysis of the skull shows that it combines many features common to modern chicken- and duck-like birds, suggesting that the ‘Wonderchicken’ is close to the last common ancestor of modern chickens and ducks. The fossil was found in a limestone quarry near the Belgian-Dutch border, making it the first modern bird from the age of dinosaurs found in the northern hemisphere.
The fossil doesn’t look like much at first glance, with only a few small leg bone fragments poking out from a piece of rock the size of a deck of cards. Even those small bones attracted the researchers’ interest, since bird fossils from this point in Earth’s history are so rare.

Using high-resolution X-ray CT scans, the researchers peered through the rock to see what was lying beneath the surface. What they saw, just one millimeter beneath the rock, was the find of a lifetime: a nearly complete 66.7-million-year-old bird skull.
“The moment I first saw what was beneath the rock was the most exciting moment of my scientific career,” said Dr. Daniel Field from Cambridge’s Department of Earth Sciences, who led the research. “This is one of the best-preserved fossil bird skulls of any age, from anywhere in the world. We almost had to pinch ourselves when we saw it, knowing that it was from such an important time in Earth’s history.
“The ability to CT scan fossils, like we can at the Cambridge Biotomography Centre, has completely transformed how we study paleontology in the 21st century.”
“Finding the skull blew my mind,” said co-author Juan Benito, also from Cambridge, who was CT scanning the fossils with Field when the skull was discovered. “Without these cutting-edge scans, we never would have known that we were holding the oldest modern bird skull in the world.”
The skull, despite its age, is clearly recognizable as a modern bird. It combines many features common to the group that includes living chickens and ducks — a group called Galloanserae. Field describes the skull as a kind of ‘mash-up’ of a chicken and a duck.
“The origins of living bird diversity are shrouded in mystery — other than knowing that modern birds arose at some point towards the end of the age of dinosaurs, we have very little fossil evidence of them until after the asteroid hit,” said co-author Albert Chen, a Ph.D. student based at Cambridge. “This fossil provides our earliest direct glimpse of what modern birds were like during the initial stages of their evolutionary history.”
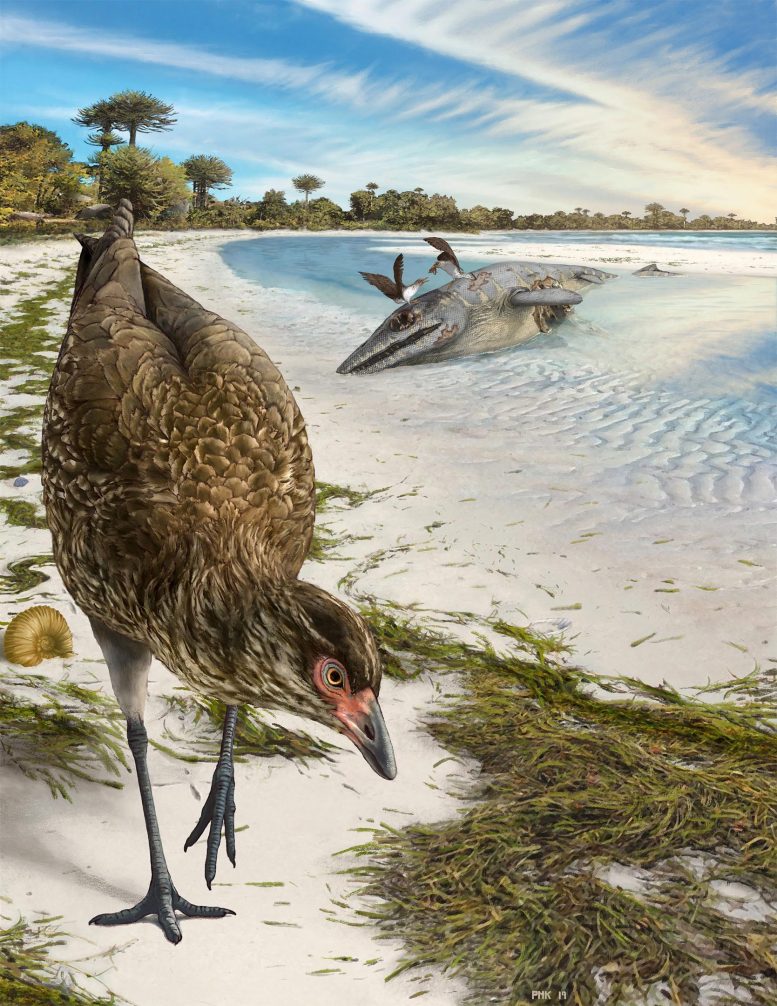
While the fossil is colloquially known as the Wonderchicken, the researchers have given it the slightly more elegant name of Asteriornis, in reference to Asteria, the Greek Titan goddess of falling stars.
“We thought it was an appropriate name for a creature that lived just before the end-Cretaceous asteroid impact,” said co-author Dr. Daniel Ksepka from the Bruce Museum in Greenwich, Connecticut. “In Greek mythology, Asteria transforms herself into a quail, and we believe Asteriornis was close to the common ancestor that today includes quails, as well as chickens and ducks.”
The fact that Asteriornis was found in Europe is another thing which makes it so extraordinary. “The late Cretaceous fossil record of birds from Europe is extremely sparse,” said co-author Dr. John Jagt from the Natuurhistorische Museum Maastricht in the Netherlands. “The discovery of Asteriornis provides some of the first evidence that Europe was a key area in the early evolutionary history of modern birds.”
“This fossil tells us that early on, at least some modern birds were fairly small-bodied, ground-dwelling birds that lived near the seashore,” said Field. “Asteriornis now gives us a search image for future fossil discoveries — hopefully, it ushers in a new era of fossil finds that help clarify how, when, and where modern birds first evolved.”
The announcement of the Wonderchicken find coincides with a new exhibit at Cambridge’s Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences, where visitors can learn more about Asteriornis and see the fossil up close. “Dawn of the Wonderchicken” runs from 19 March to 15 June. Admission is free.
Reference: “Late Cretaceous neornithine from Europe illuminates the origins of crown birds” by Daniel J. Field, Juan Benito, Albert Chen, John W. M. Jagt and Daniel T. Ksepka, 18 March 2020, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2096-0
Dr. Daniel Field is funded by a UKRI Future Leaders Fellowship. He is a University Lecturer in the Department of Earth Sciences at the University of Cambridge, and a Fellow of Christ’s College Cambridge.