A new study is the first to identify how human brains grow much larger, with three times as many neurons, compared with chimpanzee and gorilla brains. The study, led by researchers at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, UK, identified a key molecular switch that can make ape brain organoids grow more like human organoids, and vice versa.
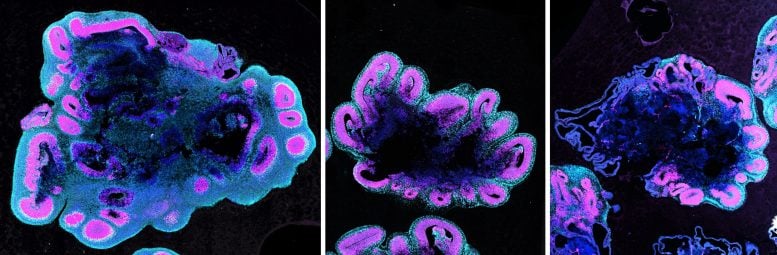
The study, published in the journal Cell, compared ‘brain organoids’ — 3D tissues grown from stem cells which model early brain development — that were grown from human, gorilla, and chimpanzee stem cells.
Similar to actual brains, the human brain organoids grew a lot larger than the organoids from other apes.
Dr. Madeline Lancaster, from the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, who led the study, said: “This provides some of the first insight into what is different about the developing human brain that sets us apart from our closest living relatives, the other great apes. The most striking difference between us and other apes is just how incredibly big our brains are.”
During the early stages of brain development, neurons are made by stem cells called neural progenitors. These progenitor cells initially have a cylindrical shape that makes it easy for them to split into identical daughter cells with the same shape.
The more times the neural progenitor cells multiply at this stage, the more neurons there will be later.
As the cells mature and slow their multiplication, they elongate, forming a shape like a stretched ice-cream cone.
Previously, research in mice had shown that their neural progenitor cells mature into a conical shape and slow their multiplication within hours. Now, brain organoids have allowed researchers to uncover how this development happens in humans, gorillas, and chimpanzees.
They found that in gorillas and chimpanzees this transition takes a long time, occurring over approximately five days.
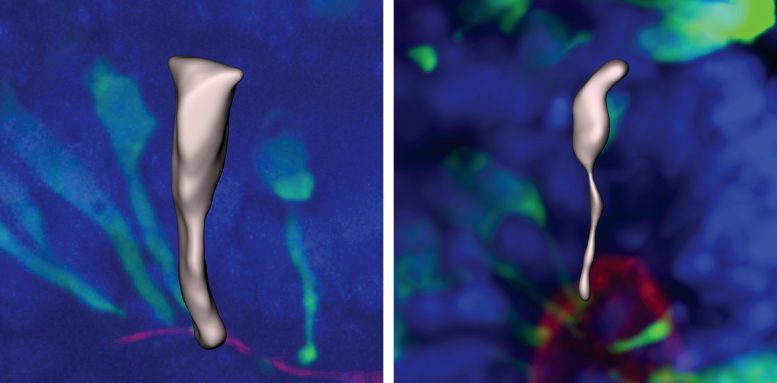
Human progenitors were even more delayed in this transition, taking around seven days. The human progenitor cells maintained their cylinder-like shape for longer than other apes and during this time they split more frequently, producing more cells.
This difference in the speed of transition from neural progenitors to neurons means that the human cells have more time to multiply. This could be largely responsible for the approximately three-fold greater number of neurons in human brains compared with gorilla or chimpanzee brains.
Dr. Lancaster said: “We have found that a delayed change in the shape of cells in the early brain is enough to change the course of development, helping determine the numbers of neurons that are made.
“It’s remarkable that a relatively simple evolutionary change in cell shape could have major consequences in brain evolution. I feel like we’ve really learnt something fundamental about the questions I’ve been interested in for as long as I can remember — what makes us human.”

To uncover the genetic mechanism driving these differences, the researchers compared gene expression — which genes are turned on and off — in the human brain organoids versus the other apes.
They identified differences in a gene called ‘ZEB2’, which was turned on sooner in gorilla brain organoids than in the human organoids.
To test the effects of the gene in gorilla progenitor cells, they delayed the effects of ZEB2. This slowed the maturation of the progenitor cells, making the gorilla brain organoids develop more similarly to human — slower and larger.
Conversely, turning on the ZEB2 gene sooner in human progenitor cells promoted premature transition in human organoids, so that they developed more like ape organoids.
The researchers note that organoids are a model and, like all models, do not to fully replicate real brains, especially mature brain function. But for fundamental questions about our evolution, these brain tissues in a dish provide an unprecedented view into key stages of brain development that would be impossible to study otherwise.
Dr. Lancaster was part of the team that created the first brain organoids in 2013.
Reference: “An early cell shape transition drives evolutionary expansion of the human forebrain” by Silvia Benito-Kwiecinski, Stefano L. Giandomenico, Magdalena Sutcliffe, Erlend S. Riis, Paula Freire-Pritchett, Iva Kelava, Stephanie Wunderlich, Ulrich Martin, Gregory A. Wray, Kate McDole and Madeline A. Lancaster, 24 March 2021, Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.050
This study was funded by the Medical Research Council, European Research Council and Cancer Research UK.
5 Comments
… “how incredibly big our brains are”//good to know…
, and how small our jaws are, and some other things,but why is that like that.
In another words, what has caused that,…
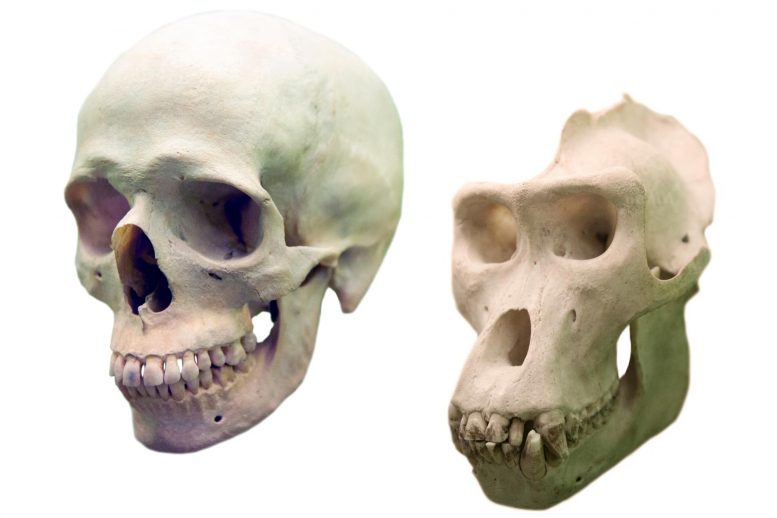
take a look at the photo of the two skulls side by side. the chimp skull has a large sagittal crest- where the jaw muscles insert. this helps the critter to eat tough foods like nuts. but it also encases the skull in strong muscle- so the brain cannot grow even if the appropriate genes are turned on. archaic hominids also had sagittal crests but of decreasing size.
in 2004, reported in Nature by Stedman- they found a mutation in the MYH16 gene that resulted in marked weakening of the muscles of mastication- hence less encasement of the skull and the brain could now grow in size.
this report demonstrates the “on switch” for brain growth so the organ- the brain- could now grow to fill the skull case no longer impeded by muscle.
it all works together
People are idiots, and beleive anything to try to run away from God.
@Eli this is god at work my friend. Life is the art, but this type of is the craft that goes behind it. Like in music, you can listen to a song or a piece and be swept away by it and know nothing of music, but the composer still has to have technical knowledge to get those specific sounds and ideas across. This is the same thing. There is room for spirituality and science.
Perhaps talking about something that has never had an agreed, self-consistent description, even among its own adherents, would be more appropriate on sites dealing with fiction rather than on a site dealing with facts and things that can be measured?