
Research indicates that the largest T. rex could have weighed up to 15 tonnes and measured 15 meters, significantly larger than any currently known specimens, suggesting potential for even larger discoveries as paleontological efforts continue.
New research published in the journal Ecology and Evolution assesses the maximum possible sizes of dinosaurs, using Tyrannosaurus rex as an example. Using computer modeling, Dr. Jordan Mallon of the Canadian Museum of Nature and Dr. David Hone of the Queen Mary University of London, produced estimates that T. Rex might have been 70% heavier than what the fossil evidence indicates.
Exploring Dinosaur Size Estimations
The huge sizes attained by many dinosaurs make them a source of endless fascination, raising the question as to how these animals evolved to be so big. There are perennial claims and counter-claims about which dinosaur species was the largest of its group or even the largest ever.
Most dinosaur species are known from only one or a handful of specimens, so it’s extraordinarily unlikely that their size ranges will include the largest individuals that ever existed. The question remains: how big were the largest individuals, and are we likely to find them?

Computer Modeling Insights
To address this question, Mallon and Hone used computer modeling to assess a population of T. rex. They factored in variables such as population size, growth rate, lifespan, the incompleteness of the fossil record, and more.
T. rex was chosen for the model because it is a familiar dinosaur for which many of these details are already well estimated. Body-size variance at adulthood, which is still poorly known in T. rex, was modeled with and without sex differences and is based on examples of living alligators, chosen for their large size and close kinship with the dinosaurs.
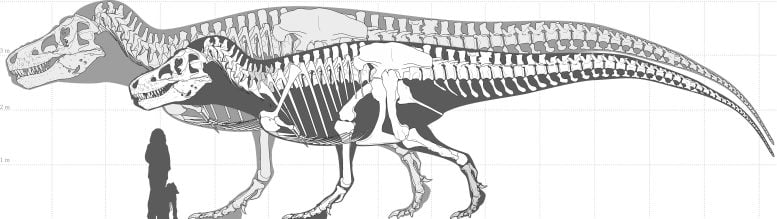
Discovering Gigantic Dinosaurs
The paleontologists found that the largest known T. rex fossils probably fall in the 99th percentile, representing the top 1% of body size, but to find an animal in the top 99.99% (a one-in-ten-thousand individual) scientists would need to excavate fossils at the current rate for another 1,000 years.
The computer models suggest that the largest individual that could have existed (one in 2.5 billion animals) may have been 70% more massive than the current largest-known T. rex specimens (an estimated 15 tonnes vs 8.8 tonnes) and 25% longer (15 meters vs 12 meters).
The values are estimates based on the model, but patterns of discovery of giants of modern species tell us there must have been larger dinosaurs out there that have not yet been found. “Some isolated bones and pieces certainly hint at still larger individuals than for which we currently have skeletons,” says Hone.

Implications of New Fossil Discoveries
This study adds to the debates about the largest fossil animals. Many of the largest dinosaurs in various groups are known from a single good specimen, so it’s impossible to know if that one animal was a big or small example of the species. An apparently large species might be based on a single giant individual, and a small species based on a particularly tiny individual—neither of which reflect the average size of their respective species.
Mallon said: “Our study suggests that, for big fossil animals like T. rex, we really have no idea from the fossil record about the absolute sizes they might have reached. It’s fun to think about a 15-tonne T. rex, but the implications are also interesting from a biomechanical or ecological perspective.”
Hone adds: “It’s important to stress that this isn’t really about T. rex, which is the basis of our study, but this issue would apply to all dinosaurs, and lots of other fossil species. Arguing about ‘which is the biggest?’ based on a handful of skeletons really isn’t very meaningful.”
The chances that paleontologists will find the largest ever individuals for a given species are incredibly small. So, despite the giant skeletons that can be seen in museums around the world, the very largest individuals of these species were likely even larger than those on display.
Reference: “Estimation of maximum body size in fossil species: A case study using Tyrannosaurus rex” by Jordan C. Mallon and David W. E. Hone, 24 July 2024, Ecology and Evolution.
DOI: 10.1002/ece3.11658
3 Comments
Visit us Telkom University
What is the main concern regarding the horror story app?
Visit us Telkom University
Which of the following is a possible consequence of the data leak?
Greeting : Telkom UniversityWhat kind of data might have been leaked from the app?